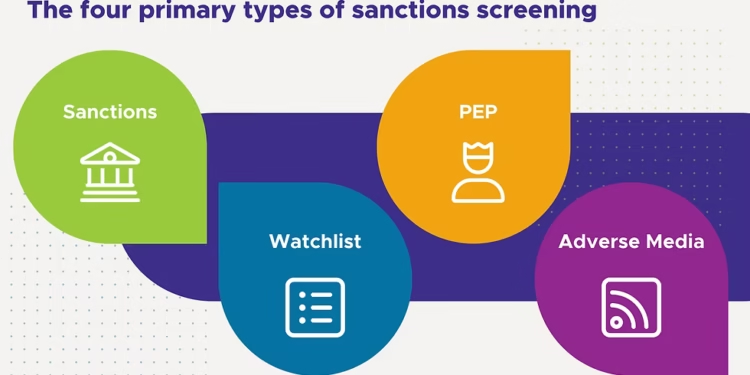
Since financial compliance keeps changing, businesses are expected to be constantly on the alert and protect themselves against financial crimes like money laundering, corruption and terrorism financing. Two important elements needed in a robust AML framework include PEP screening and sanctions screening. Notwithstanding their common reference, their roles and the emphasis of regulation are dissimilar. Comprehending their differences is crucial for organizations who wish to continue being compliant and to lower risk exposure.
In this article, we will see the distinction between PEP screening from sanctions list screening, discuss the importance of each for mitigating risks, and share effective implementation strategies for each.
Contents
What is PEP Screening?
Politically Exposed Person (PEP) screening is an identity verification process that seeks to identify the individuals and their relatives or those they trust who either have served or presently serve in high-level positions of office within the government or public sphere. The concern arises from the fact that such people are more susceptible to corruption, bribery, or using their positions to gratify their own interests.

Who Qualifies as a PEP?
- strong
- Heads of state or government
- Senior politicians
- High-ranking military officials
- Senior executives of state-owned corporations
- Judiciary members
- Close relatives and important associates of prominent people
One must understand that a person who is considered a PEP is not a person who has committed some criminal acts. As those with PEP status are more exposed, financial institutions need to carry out PEP checks to guarantee the strict due diligence.
What is Sanctions Screening?
Sanctions screening is the term for the systematic examination of individuals, businesses, and countries against lists of entities under severe regulatory constraints provided by governmental and worldwide organizations. These lists consist of individuals and organizations that are legally or financially limited due to their involvement in activities such as terrorism, arms trafficking, or massive human rights violations.
Examples of Sanctions Lists:
- United States Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC)
- UN Security Council Sanctions List
- EU Sanctions List
- HM Treasury Sanctions List (UK)
Failure to comply with sanctions screening requirements poses significant financial risks and can damage a company’s reputation, which is why it is a critical part of compliance screening programs.
Understanding the Distinctiveness of PEP Screening versus Sanctions Screening
Despite some shared compliance processes in PEP screening and sanctions screening, the aims behind them and target audiences are different.
- Feature
- PEP Screening
- Sanctions Screening
- Purpose
- Target politically risky people.
- Identify organizations or persons subject to legal or economic limitations
- Focus
- Risk-based (enhanced due diligence)
- Rule-based (strict legal compliance)
- Source Lists
International networks of politically exposed person databases which are collected from official agencies, media outlets, and open sources.
Government issued and international sanctions databases
- Legal Obligation
- Even though mandatory, FATF and regulatory bodies advise it as best practice.
- Legally required by jurisdictional law
- Ongoing Monitoring
- Recommended for changes in status
- Mandatory for updated sanctions lists
- Implications
- other option
can turn out to do so by blocking payments or terminating partnerships.
Why Both Screenings Are Critical
Politically exposed person screening and sanctions list filtering, although having independent functionalities, are critical in the creation of a robust AML screening architecture. Here’s why:
1. Risk Management
Politically exposed persons (PEPs) can cause reputational or corruption problems and businesses may suffer legal and financial penalties when transacting with sanctioned individuals or entities. The execution of both screenings offers institutions crucial information to inform their risk management strategies.
2. Regulatory Compliance
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), the U.S. Treasury, and the European Union, among others, require complete screening procedures. There are serious fines and sanctions that can be imposed on the institution if it fails to comply.
3. Reputation Protection
One loophole in compliance screening can lead to the negative publicity, which will make customers lose confidence in your institution. An insistence on PEP and sanctions checks is an example of a business’s commitment to ethics.
Main Techniques for Effective PEP and Sanctions Screening
To enhance their AML compliance framework, organizations should adhere to the following best practices:
1. Use Reliable Data Sources
Collect PEP information from reliable global databases that are always updated. Companies have to turn to official and authoritative databases from OFAC, EU, or UN for their sanctions data.
2. Implement Real-Time Screening
Failure to recognize a newly sanctioned entity or change in a person’s PEP standing in a timely manner puts businesses at significant risk. Real-time monitoring ensures immediate action.
3. Apply Risk-Based Approaches
Sanctions screening is based on the strict compliance with fixed regulations, but PEP screening should be flexible in accordance with possible risks. There is a difference in the risk presented by each PEP.
4. Maintain Ongoing Monitoring
The classification of an individual as a politically exposed person (PEP) can change, like the changes made to ongoing sanctions lists. Automated tools implementation systemizes screening process and provides a possibility for organizations to monitor updates effectively.
5. Train Staff Regularly
Confirm that your compliance personnel are well informed on the differences of PEP and sanctions checks, and the ability to manage screening alert notifications.
Frequent Problems and Solutions for Implementation
While faced with continued technology development, companies continue to grapple with several critical issues in implementing PEP and sanctions screening,<<
False Positives
False positive alerts may be triggered by similar-sounding names. Utilize software that can furnish additional details such as date of birth, nationality or occupation to reduce the number of false alerts.
Data Overload
Dealing with volumes of screening results can soon become daunting. Using automation and improved filtering systems may streamline your screening processes and alert you to possible red flags.
Global Coverage
The global growth involves screening against regulatory lists of a number of countries, each using different languages. Choose screening tools that offer multilingual support and include all relevant regulatory lists.
Conclusion
PEP screening and sanctions screening are important in the fight against financial crime. In spite of the fact that they deal with separate risks – for example, PEPs in case of corruption issues and sanctions in case of compliance issues – they are important in protecting your organization from violations of regulation and reputational harm.
Understanding the difference and combining both practices allows organizations to develop a holistic and future-oriented method of AML compliance. The assurance that your organization is using reliable tech, has strict monitoring and has a constant training of staff is the key to satisfying regulatory requirements and keeping the trust of both the clients and stakeholders.